TABLE OF CONTENT
What is a Python Web App?
Building a Python Web App: 8 Simple Steps for You
Key Benefits of Python Web App
5 Prominent Names as Top Python Web App Examples
Conclusion
What is a Python Web App?
Python web app is a dynamic software application developed using the Python programming language.
It takes advantage of Python-specific libraries and frameworks, such as Flask or Django, to create secure, maintainable, and scalable web applications. Frameworks also simplify the web app development process with integrated functions such as user authentication, URL routing or database management.
Python web app can also serve content to users very efficiently. This programming language allows business owners to enjoy its flexibility, power, easy-to-read syntax, and extremely active community support throughout the process of building and running a Python web app.
Building a Python Web App: 8 Simple Steps for You
When deciding to create a Python web app, you need to understand the steps below to easily speed up this process:

Step 1: Clearly define goals
Before proceeding with each specific step in the process of building a Python web app, it is extremely important that you clearly define your goals. You need to make sure the web app you create truly fits your business goals and user needs.
- Determine the purpose of this Python web app: clearly identify the purpose for which you are building the web app. Is it an ecommerce platform, a social media site, a content development and management system, or a custom application for internal business solutions? Clearly defining your purpose will help you orient your development path more clearly and accurately.
- Thoroughly research the target audience: conduct research on all aspects of the target audience, from demographics, preferences when using the web app, technical level or possible limitations. It creates a Python web app design that is always user-centric.
- List the main features and functions of the application: some must-have features should be listed to avoid emissions during the build process, such as user registration/login, updates and reporting real-time data, publish content, showcase user interactions. Prioritize features based on your research and decisions about intended use and target audience.
- Plan clearly your timelines and operating budget: outline as thoroughly as possible the expected budget and time frame for Python web app development. Carefully consider the maximum costs for each work item such as development, testing, deployment and maintenance after going live.
Step 2: Choose the appropriate framework
Choosing the right framework will also depend on the complexity and development scale of your Python web app. The right framework will help you optimize your development process, easily implement best practices, and deliver the best results for your business.
Some of our suggestions below will help you shorten this process as much as possible:
- Choose Django for comprehensive solutions: Django is a Python web framework with special integration features, such as ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) for database interaction, powerful user authentication system and internal logic interface from A-Z. It is suitable for applications that need a lot of built-in functions such as social networks or ecommerce platforms.
- Choose Flask for its outstanding flexibility and simplicity: Flask is a lightweight, highly customizable micro-framework. It’s ideal for small applications that don’t require much initial bloat and help you better manage individual components.

For example, if you just need to create a simple blog or RESTful API for your mobile app, you might consider using Flask to quickly build and easily deploy that blog.
In addition to the two outstanding frameworks above to create a Python web app, you can refer to other frameworks. Make your choice based on your actual needs and goals of your web app:
- Pyramid: stands out with flexible features and extensive development capabilities, like a balanced combination of Django and Flask. It is suitable for a Python web app that is starting out on a small or mid-range scale, but is expected to quickly scale up and dramatically develop features in the near future.
- FastAPI: perfect for high-performance applications that involve a lot of asynchronous operations. It is designed to build APIs with modern Python capabilities that can handle concurrency in a truly efficient manner.
Step 3: Set up a comprehensive development environment

Set up a comprehensive development environment to help your Python web app quickly become stable, streamlining coding, testing or debugging processes that arise.
- Install Python and a comprehensive management panel: make sure you have Python installed on your machine, and use managers platforms like pyenv to be able to manage multiple versions of Python at the same time. It helps you easily switch between different applications without spending too much time.
- Set up virtual environment: use virtual environment to separate project dependencies, and at the same time, avoid conflicting reactions of different applications. The most commonly used tools include venv or virtualenv.
- Install libraries and integrate necessary tools: fully install essential features for development, such as selected framework (Django, Flask), database drivers (SQLite, PostgreSQL) and other necessary parts.
- Set up a code editor or IDE: choose a suitable code editor or IDE (Integrated Development Environment) to support the development of your Python web app with specific features such as code completion, syntax highlighting or debugging error. A few options worth considering are PyCharm, Visual Studio Code (VS Code), and Sublime Text.
- Use version control systems: you should learn and choose reputable application control systems to track periodic changes, collaborate with team members and manage code versions differently. Platforms like GitLab, GitHub or Bitbucket help store your application information repository really effectively.
- Identify and install debugging tools: tools like pdb (for debugging), or pytest (for extensive performance testing of the entire application) should be used extensively throughout the entire Python web app development process.
- Set up automation tools: determining the use of automation tools right from the beginning will help you greatly optimize operating and development time. You can use Makefiles, task runners like Invoke, or shell scripts to automate some special tasks like running application tests, automated application deployment, or writing source code.
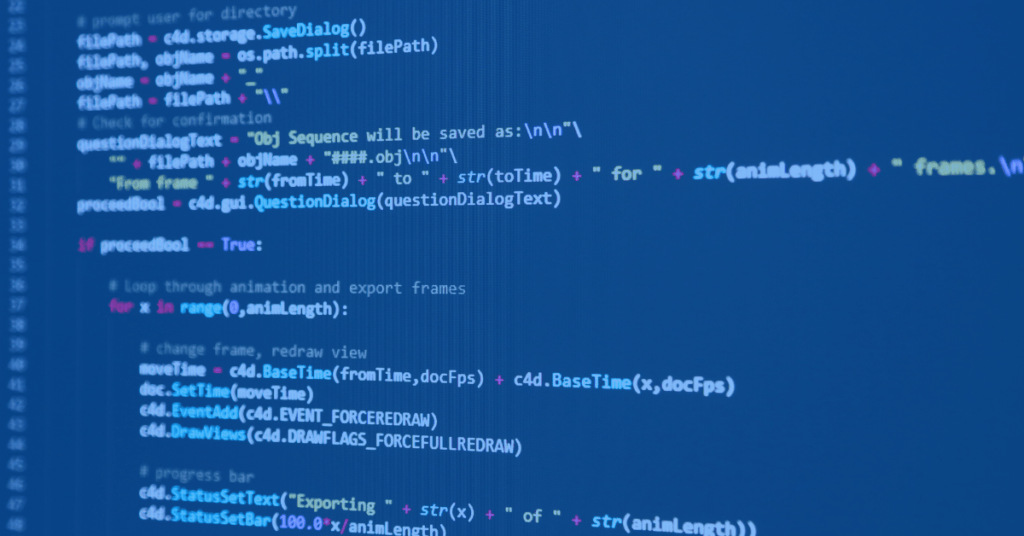
Step 4: Design your database schema
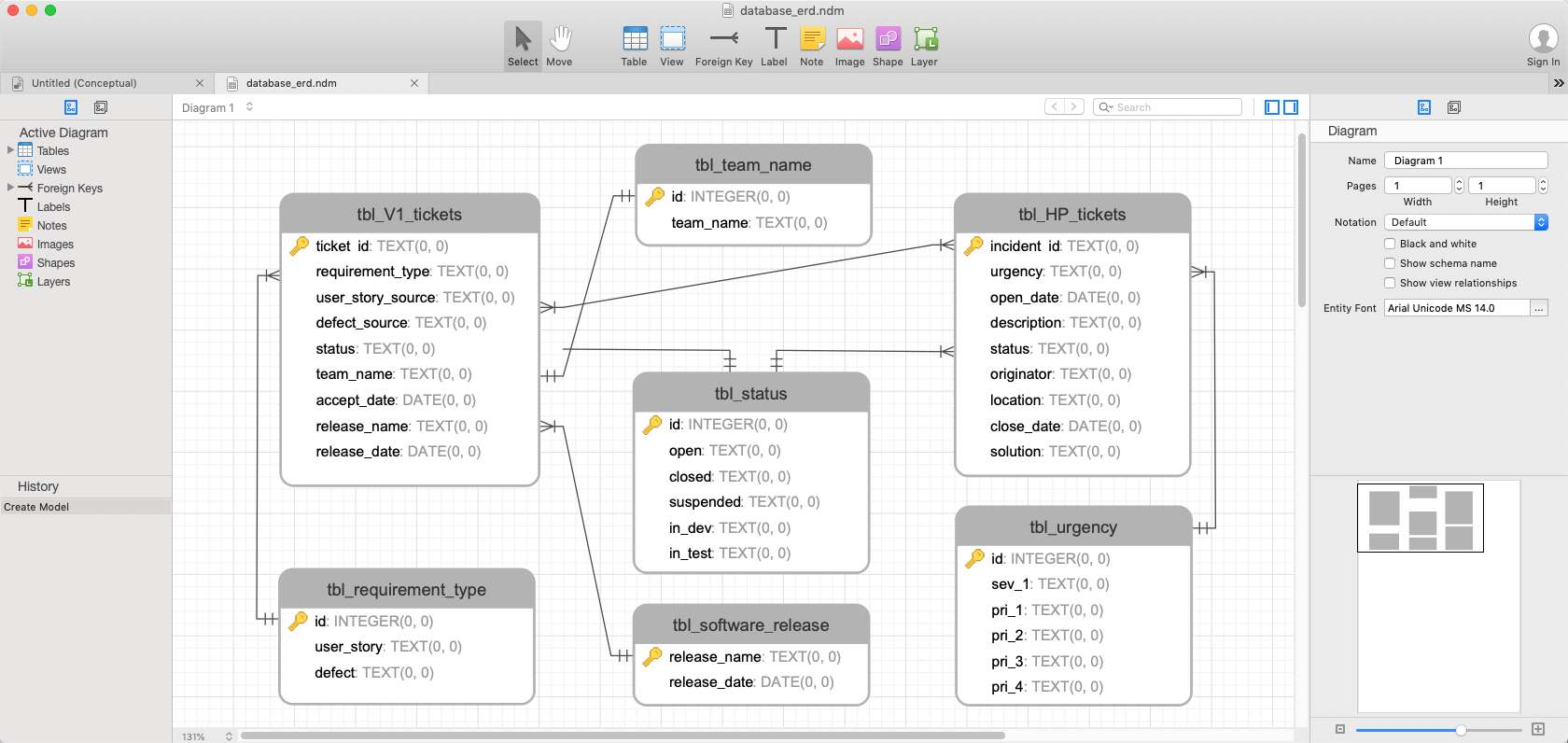
Depending on the requirements when building a Python web app, you will choose the appropriate databases to set up and develop locally. If only for light development purposes, you can consider SQLite. However, if you need a more powerful database, use MySQL or PostgreSQL.
An example code to install and set up PostgreSQL, then configure Django to connect to it in settings.py:
DATABASES = {
‘default’: {
‘ENGINE’: ‘django.db.backends.postgresql’,
‘NAME’: ‘mydatabase’,
‘USER’: ‘mydatabaseuser’,
‘PASSWORD’: ‘mypassword’,
‘HOST’: ‘localhost’,
‘PORT’: ‘5432’,
}
}
Besides, you also need to ensure data integrity at all times, both before, during and after the Python web app deployment process by using constraints such as Not Null, Check, Unique and Foreign Key. These constraints will ensure data consistency and validity throughout operations.
Step 5: Develop important functions
Once you’ve completed the setup and database settings for your Python web app, you need to consider developing the essential operations and features that users will experience firsthand.
- User authentication: in the Registration and Login section of your Python web app, you should implement it carefully because it is the first part that impresses customers when accessing the application. Ensure items such as setting passwords securely and safely, or managing user sessions at a fixed time to authenticate access and to limit foreign attacks.
- CRUD operations: don’t forget to develop CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete). These functions will help ease the process of interacting with databases on Python web app.

- Error handling and data validation: quickly implement data validation, ensuring that data entered by users is accurate and in expected formats. At the same time, this action also helps handle errors skillfully and ensures a seamless experience for users.
- Notifications to users: ensure that the system to send automatic notifications to users will be easily enabled on the Python web app. The channels used can be via email, in-app or other social channels depending on the goals of your campaign.
For example, when using Django to send an email to the application’s customers, notifying them that a post has just been created, you can use the following code recommended by our mobile app developer:
from django.db.models.signals import post_save
from django.dispatch import receiver
from django.core.mail import send_mail
from .models import Post
@receiver(post_save, sender=Post)
def notify_admin(sender, instance, created, **kwargs):
if created:
send_mail(
‘New Post Created’,
f’A new post titled “{instance.title}” has been created.’,
‘from@example.com’,
[‘admin@example.com’]
)
- Build search and filtering tools: Customized search and filtering functions are what many customers look for in a perfect Python web app. Spend a lot of time developing the search and filtering functions of your application to improve and perfect its quality when put into real use.
- API development: Create APIs to allow integrated applications or services to easily interact with your Python web app. To do that, you might consider using REST or GraphQL standards to design your API.
Step 6: Build the user interface
Building the user interface (UI) is an important step in the development process of your Python web app. Its quality directly affects how users reach and interact with your application. What you need to do is:
- Design wireframes and mockups: create wireframes that roughly outline the basic structure and layout of the application interface. The tools you can use can be Sketch, Figma or Adobe XD, to visually represent the look and feel of your desired application before diving into implementation.
- Choose a front-end framework: choose a front-end framework that can integrate well with your backend features. Popular frameworks include Angular, React, and Vue.js. You can also consider simpler ones like Bootstrap, which focus on simple and responsive designs.
- Implement a quality-assured user interface: ensure that your user interface is responsive, adapting seamlessly across multiple channels and devices. To do that, use query facilities and response units (like ems or percentages), ensuring the responsiveness of your Python web app. Besides, make sure the interface is user-friendly enough, and complies with web content accessibility guidelines (WCAG).
- Ensure consistency with brand personality: use typography, colors and design elements across all Python web app designs that are consistent with the brand identity. This helps customers have a deep memory of your brand as soon as they enter your own digital store, while also affirming the professionalism of your business.
Step 7: Check and thoroughly review the quality of the web app
After you have preliminarily completed the desired content, you should spend a certain amount of time thoroughly checking, reviewing and testing the Python web app version.

- Make sure all features and functions work smoothly.
- Develop tests to validate individual components in the code base. Use testing frameworks like pytest for Python web app to automate management processes, easily isolating and testing specific units of code.
- Test performance to make sure your Python web app can handle the load at high speeds, with tools like JMeter or Locust. They help simulate high traffic and measure web app times, thereby identifying areas where the app can be improved.
- Check security quality deeply, especially common security errors such as SQL, CSRF (cross-site request forgery) or XSS (cross-site scripting). You can use tools like Burp Suite or OWASP ZAP for a comprehensive security assessment.
- Test the visibility of Python web app on different browsers (Chrome, Safari, Edge, Firefox) and different connected devices (desktop, laptop, iPad, mobile devices). Really consider the layout, responsiveness, and functionality issues on each platform to ensure a seamless user experience.
Step 8: Publish the app and continuously monitor performance
After testing the beta version and ensuring it meets all expectations according to the initial mission set, you and your team should be ready to publish the app. It’s the perfect time for the team to have a big win!
- Identify the hosting provider for this Python web app, which can be Google Cloud, AWS, or Microsoft Azure.
- Publish the application, ensuring all features are successfully integrated and can run smoothly immediately after successful publishing.
- Closely monitor performance-related issues such as response times, error rates, traffic patterns. You can use monitoring solutions like Grafana, New Relic, Prometheus, or Datadog to better understand application performance.
- Set up anomaly alerts via SMS, email, or communication platforms like Microsoft Teams or Slack. This helps you quickly detect errors, minimize downtime, and maintain customer satisfaction.
Key Benefits of Python Web App
There are many reasons for your business to decide to build and develop a Python web app. It brings more special benefits than you think:

Flexibility
Python owns a huge ecosystem of many libraries with featured frameworks such as Flask, Django and Pyramid. It can meet many special requirements in the process of building web applications, including specialized blogs, ecommerce platforms or data analysis tools.
Supportive community and rich resources
Python owns a large global developer community, with abundant resources. Businesses have the opportunity to acquire knowledge, seek strong community support, comprehensively exchange and collaborate with reputable partners in the Python circle.
Integrate with new technologies
Connecting and integrating with new technologies such as machine learning, data analytics or artificial intelligence through libraries such as TensorFlow, PyTorch or scikit-learn helps your Python web app seamlessly integrate advanced capabilities easily. Besides, personalizing customer experience also becomes not too difficult.
Ability to develop rapidly
Python uses crisp, concise and clear syntax, shortening web app development time. Developers can write concise, easy-to-read code, minimizing development time and effort. Frameworks like Django also provide built-in features for common web development tasks like URL routing, database validation, feature integration, which further speeds up the development process.
5 Prominent Names as Top Python Web App Examples
The 5 Python web apps from famous brands below will help you have a more specific view of the interface, how they are built and the effectiveness they have achieved.

Instagram is a popular photo sharing Python web app globally with billions of users.
This app is built with Django and uses the Python programming language in various tasks, like implementing annotations for its HTTP API, creating a static sort checking browser. It makes it easy for Instagram to expand and grow radically, keeping up with the accelerating pace of modern users.

Reddit has successfully utilized Python in its special features such as readability, writability, and the wide range of available libraries it provides. Reddit’s founder also heaped praise on Python’s clear structure, which simplifies code review and maintenance, while ensuring it always operates smoothly and efficiently.
Spotify

Spotify is an online music streaming platform with about 615 million users. One thing that few people know is that Spotify is built based on the Python language (applied from June 2022) to forecast user trends. With strong support and flexibility, Python allows Spotify to quickly handle backend services, analyze data, and act on machine learning applications. This maximizes the user experience when listening to music.

Facebook is a social Python web app that is so popular among global users. Extremely large and with increasing development needs, Facebook still decided to use Python to develop web apps as well as ensure the effectiveness of machine learning applications. According to Netguru, Meta Platforms, Facebook’s parent company, also donated $300,000 to the Python Software Foundation, affirming its trust and need for long-term companionship.
Netflix

One of the biggest strengths of Netflix, the globally popular platform for streaming films and TV shows, is its powerful analytics and personalized recommendations for users. Almost all are built on Python. The intuitive nature of this language allows to ease the process of developing machine learning engines, exploring data, and automatically analyzing and statistical user behavior. This helps Netflix understand what areas it needs to focus on and how to develop it to continue attracting customers.
Conclusion
Python web app is a great choice for businesses looking to position themselves quickly and deeply in the technology market. Python asserts itself as a programming language with many advantages, neat, simple, easy to analyze, easy to extend and develop with a large support community.
However, don’t forget that it itself is still a software programming language, and to use it truly effectively, you and your team are required to have certain knowledge in the software and each feature it can integrate. To build a Python web app, don’t just read an article. You can look for a reputable consulting unit to receive customized advice after they carefully review your business situation and your desire to develop a web app, tied to each specific time frame.
AHT Tech is always still here and ready to help you. Over 16 years, we have successfully conducted a perfect web app development process based on the most advanced technologies, with end-to-end solutions and high-skilled experts. AHT Tech confidently brings you the best consulting service and professional operating process from A-Z to create a perfect Python web app.
Contact us immediately for more detailed information about creating Python web app service!



